Evaluation on the system of service organization for new agricultural modernization in Henan Province and its rules of spatial distribution
-
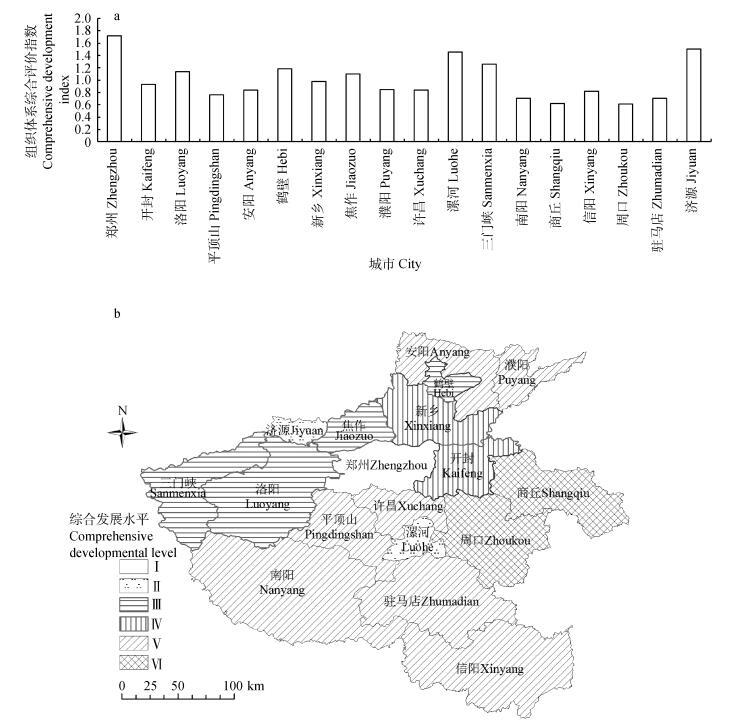
摘要: 基于2014年中央提出的农业发展“三个导向”要求,本文构建了由土地流转、资源配置、信息服务、产业管理“四大组织”构成的新型农业现代化服务组织体系评价模型,以河南省18个市为基本单元,对服务组织体系的综合发展水平进行了评价,并探讨了空间分布规律。结果表明:河南省新型农业现代化服务组织体系整体发展水平较低,进入Ⅰ、Ⅱ类地区的只有3个市(郑州、济源、漯河),其余15个市集中在Ⅲ、Ⅳ、Ⅴ、Ⅵ类地区。空间分布有一定规律,豫西整体水平较高,洛阳、济源、焦作、三门峡都在Ⅱ或Ⅲ类地区;其次为豫中,郑州、漯河分别进入Ⅰ、Ⅱ类地区,但许昌、平顶山均在Ⅴ类地区;再次为豫北,鹤壁进入Ⅲ类地区,新乡、安阳、濮阳却停留在Ⅳ、Ⅴ类地区;然后为豫南,南阳、信阳、驻马店都处于Ⅴ类地区;最后为豫东,商丘、周口均为Ⅵ类地区,开封也只进入Ⅳ类地区。研究表明,河南省应构建完善的新型农业现代化服务组织体系,引导农地规模化流转,提高生产经营组织化程度,推进农业发展方式转变,保障农产品质量数量安全,这是加快农业现代化发展的必然选择。Abstract: Based on the requirements of agricultural development in line with the"Three Orientations"strategy presented by China's Central Government in 2014, an evaluation index system on the system of service organization for new agricultural modernization were established.With Henan Province as the case study, the paper explored the development level and the rules of spatial distribution of service organization system, aiming to provide references for its further improvement.The index system was consisted of 16 indexes included in 4 criteria layers, which were development indexes of rural land circulation organization, resources allocation organization, information service organization and industrial management organization.Then using 18 cites in Henan Province as the basic units, the comprehensive development level of service organization system, and the related rules of spatial distribution were determined.The results showed that the comprehensive development level of service organization system was low in Henan Province.Only Zhengzhou, Jiyuan and Luohe were in District Ⅰ and Ⅱ, and all the other 15 cities were in District Ⅲ, Ⅳ, Ⅴ and Ⅵ.The rules of spatial distribution of the 18 cities were regular.The development in western Henan was the highest, which included Luoyang, Jiyuan, Jiaozuo and Sanmenxia, all of which occurred under District Ⅱ or Ⅲ.The development in the central part ranked the second, where Zhengzhou and Luohe occurred under District Ⅰ or Ⅱ, while both Xuchang and Pingdingshan occurred under District Ⅴ.The development in the northern part ranked the third, where Hebi occurred under District Ⅲ and then Xinxiang, Anyang and Puyang all were under District Ⅳ or Ⅴ.The development in the southern part ranked fourth, where Nanyang, Xinyang and Zhumadian were under District Ⅴ.The development in the eastern part was the lowest, where both Shangqiu and Zhoukou were in District Ⅵ and Kaifeng was in District Ⅳ.The research showed that a perfect service organization system for new agricultural modernization should be established in Henan Province to guide large-scale circulation of rural land, increase organizational degree of line operation, promote agricultural transformation development and guarantee quantity and quality of agricultural products.It was an inevitable option to accelerate the development of agricultural modernization in the study area.
-
表 1 新型农业现代化服务组织体系评价指标体系
Table 1 Evaluation index system of the service organization system for new agricultural modernization
综合指标层(A)
Comprehensive criteria layer一级指标层(B)
First criteria layer二级指标层(C)
Second criteria layer新型农业现代化服务组织体系综合发展指数(A)
Comprehensive development index of the service organization system for new agricultural modernization土地流转组织发展指数(B1)
Development index of rural land circulation organization第一产业从业人员人均耕地面积(C1)
Cultivated land per capita for employee in primary industry单位面积耕地农业资金投入量(C2)
Agricultural capital investment per unit area of cultivated land农村每万人拥有农民专业合作社数量(C3)
Number of specialized farmers cooperatives every ten thousand rural people工业化水平(C4)
Level of industrialization资源配置组织发展指数(B2)
Development index of resources allocation organization农村每万户拥有市级重点龙头企业数(C5)
Cities’ key leading enterprise number in agriculture every ten thousand rural households单位耕地面积农业财政预算支出(C6)
Agricultural financial budget expenditure per unit area of cultivated land农村每万人拥有科技人员数(C7)
Scientific and technical personnel every ten thousand rural people第一产业从业人员人均产值(C8)
Output value per capita for employee in primary industry信息服务组织发展指数(B3)
Development index of information service organization信息服务业固定资产投资额比重(C9)
Ratio of fixed asset investment on information service industry互联网用户比重(C10) Ratio of internet users 人均电信业务量(C11)
Telecommunication consumption per capita信息服务人员比重(C12)
Ratio of employee in information service industry产业管理组织发展指数(B4)
Development index of industrial management organization单位耕地面积化肥施用量(C13)
Fertilizer consumption per unit area of cultivated land地理标志农产品生产面积比重(C14)
Ratio of planting area for geographical indications products第一产业从业人员人均畜肉制品产量(C15)
Animal meat products yield per capita in primary industry单位耕地拥有亿元以上商品交易市场摊位数(C16)
Number of commodity market stalls over 100 million per unit area of cultivated land表 2 2009—2013年河南省18市新型农业现代化服务单向组织发展指数和水平比较
Table 2 Developmental indexes and levels of individual organization for new agricultural modernization of 18 cities of Henan Province from 2009 to 2013
区域
Region市
City土地流转组织发展指数(B1)
Development index of rural land circulation organization资源配置组织发展指数(B2)
Development index of resources allocation organization信息服务组织发展指数(B3)
Development index of information service organization产业管理组织发展指数(B4)
Development index of industrial management organization数据Value 水平Level 数据Value 水平Level 数据Value 水平Level 数据Value 水平Level 豫中
Central Henan郑州Zhengzhou 1.132 Ⅲ 2.103 Ⅰ 2.644 Ⅰ 1.532 Ⅲ 漯河Luohe 0.822 Ⅳ 2.168 Ⅰ 1.020 Ⅳ 2.546 Ⅰ 许昌Xuchang 0.906 Ⅳ 1.083 Ⅲ 0.634 Ⅵ 0.438 Ⅵ 平顶山Pingdingshan 0.849 Ⅳ 0.767 Ⅳ 0.666 Ⅵ 0.584 Ⅴ 豫东
Eastern Henan开封Kaifeng 0.775 Ⅴ 0.575 Ⅳ 1.106 Ⅲ 2.029 II 商丘Shangqiu 0.716 Ⅴ 0.585 Ⅳ 0.619 Ⅵ 0.381 Ⅵ 周口Zhoukou 0.799 Ⅴ 0.430 Ⅴ 0.621 Ⅵ 0.435 Ⅵ 豫南
Southern Henan南阳Nanyang 0.839 Ⅳ 0.547 Ⅳ 0.782 Ⅴ 0.540 Ⅴ 信阳Xinyang 1.049 Ⅲ 0.603 Ⅳ 0.798 Ⅴ 0.601 Ⅴ 驻马店Zhumadian 0.892 Ⅳ 0.578 Ⅳ 0.653 Ⅵ 0.519 Ⅴ 豫西
Western Henan洛阳Luoyang 1.148 Ⅲ 0.975 Ⅳ 1.430 II 1.070 Ⅳ 焦作Jiaozuo 1.193 Ⅲ 1.187 Ⅲ 1.021 Ⅳ 0.707 Ⅴ 济源Jiyuan 1.443 Ⅰ 1.643 Ⅱ 1.397 II 1.281 Ⅳ 三门峡Sanmenxia 1.187 Ⅲ 1.275 Ⅲ 1.223 Ⅲ 1.480 Ⅳ 豫北
Northern Henan鹤壁Hebi 1.321 Ⅱ 1.245 Ⅲ 0.713 Ⅴ 1.233 Ⅳ 新乡Xinxiang 1.069 Ⅲ 0.806 Ⅳ 0.987 Ⅳ 1.049 Ⅳ 安阳Anyang 0.961 Ⅳ 0.616 Ⅳ 1.237 Ⅲ 0.418 Ⅵ 濮阳Puyang 0.898 Ⅳ 0.919 Ⅳ 0.927 Ⅳ 0.407 Ⅵ -
[1] 孔祥智, 周振. "三个导向"与新型农业现代化道路[J].江汉论坛, 2014, (7):42-49 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JHLT201407007.htm Kong X Z, Zhou Z. "Three Orientations" and the road of new agricultural modernization[J]. Jianghan Tribune, 2014, (7):42-49 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JHLT201407007.htm
[2] 张正斌, 段子渊, 徐萍, 等.安徽省粮食安全及现代农业发展战略[J].中国生态农业学报, 2016, 24(9):1161-1168 http://www.ecoagri.ac.cn/zgstny/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=2016902&flag=1 Zhang Z B, Duan Z Y, Xu P, et al. Development strategy for food security and modern agriculture in Anhui Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2016, 24(9):1161-1168 http://www.ecoagri.ac.cn/zgstny/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=2016902&flag=1
[3] 骆世明.农业生态转型态势与中国生态农业建设路径[J].中国生态农业学报, 2017, 25(1):1-7 http://www.ecoagri.ac.cn/zgstny/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20170101&flag=1 Luo S M. Agroecology transition and suitable pathway for eco-agricultural development in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2017, 25(1):1-7 http://www.ecoagri.ac.cn/zgstny/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20170101&flag=1
[4] 张永勋, 闵庆文, 王维奇, 等.农户社会经济特征对农业种植意愿的影响——基于农业文化遗产保护目的的福州茉莉种植户研究[J].中国生态农业学报, 2016, 24(12):1714-1721 http://www.ecoagri.ac.cn/zgstny/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20161214&flag=1 Zhang Y X, Min Q W, Wang W Q, et al. Impact of household social-economic characteristics on the willingness to grow crops:A case study of jasmine growers in Fuzhou based on conservation of the agricultural heritage system[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2016, 24(12):1714-1721 http://www.ecoagri.ac.cn/zgstny/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20161214&flag=1
[5] 张正斌, 徐萍, 段子渊.粮食安全应成为中国农业现代化发展的终极目标[J].中国生态农业学报, 2015, 23(10):1215-1219 http://www.ecoagri.ac.cn/zgstny/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20151001&flag=1 Zhang Z B, Xu P, Duan Z Y. Food security should be the ul-timate goal of agricultural modernization in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2015, 23(10):1215-1219 http://www.ecoagri.ac.cn/zgstny/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20151001&flag=1
[6] 速水佑次郎, 弗农·拉坦. 农业发展的国际分析[M]. 郭熙保, 张进铭, 译. 北京: 中国社会科学出版社, 2000: 42-45 Yujiro Hayami, VernonW.Ruttan. Agricultural Development:An International Perspective[M]. Guo X B, Zhang J M, Trans. Beijing:China Social Sciences Publishing House, 2000:42-45
[7] 尉郁.国外农村土地承包经营权流转的经验与启示[J].改革与战略, 2015, 31(5):165-167 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GGZY201505030.htm Wei Y. The experience and enlightenment of foreign rural land circulation[J]. Reformation & Strategy, 2015, 31(5):165-167 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GGZY201505030.htm
[8] 王志章, 兰剑.农村土地流转中介组织的培育与发展问题研究[J].中共南京市委党校学报, 2010, (1):64-69 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGNB201001010.htm Wang Z Z, Lan J. On cultivating and developing interme-diary organizations of rural land[J]. Journal of Nanjing Party Institute of CPC, 2010, (1):64-69 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGNB201001010.htm
[9] 温修春.中介组织视角下我国农村土地银行产生的博弈分析[J].江苏大学学报:社会科学版, 2015, 17(1):87-92 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSLD201501013.htm Wen X C. A game analysis of China's rural land bank's gen-eration based on the theory of intermediary organization[J]. Journal of Jiangsu University:Social Science Edition, 2015, 17(1):87-92 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSLD201501013.htm
[10] 西奥多·舒尔茨. 改造传统农业[M]. 梁小民, 译. 北京: 商务印书馆, 1987: 35-38 Schultz T W. Transforming Traditional Agriculture[M]. Liang X M, Trans. Beijing:The Commercial Press, 1987:35-38
[11] Reardon T, Barrett C B. Agroindustrialization, globalization, and international development:An overview of issues, pat-terns, and determinants[J]. Agricultural Economics, 2000, 23(3):195-205
[12] 汪爱娥, 包玉泽.农业产业组织与绩效综述[J].华中农业大学学报:社会科学版, 2014, (4):70-75 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HZND201404014.htm Wang A E, Bao Y Z. Review on agricultural industrial or-ganization and performance[J]. Journal of Huazhong Agri-cultural University:Social Sciences Edition, 2014, (4):70-75 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HZND201404014.htm
[13] 张玲.河北省农业经营组织发展创新研究[J].人民论坛, 2014, (35):226-228 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-3381.2014.35.072 Zhang L. Development and innovation of organization of agricultural operation in Hebei Province[J]. People's Tribune, 2014, (35):226-228 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-3381.2014.35.072
[14] 杨洪伟, 纪建伟, 李晓辉.辽宁省农业信息化服务创新体系及发展研究[J].湖北农业科学, 2016, 55(2):532-535 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HBNY201602068.htm Yang H W, Ji J W, Li X H. Research on agricultural in-formatization service innovation system in Liaoning Province and its development[J]. Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 55(2):532-535 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HBNY201602068.htm
[15] 赵洪亮. 基于资源整合的农业信息服务平台构建与实现[D]. 沈阳: 沈阳农业大学, 2012: 25-28 Zhao H L. Construction and implementation of agricultural information service platform based on resource integrat-ed[D]. Shenyang:Shenyang Agricultural University, 2012:25-28
[16] Lee H L, Billington C. The evolution of supply-chain-management models and practice at Hew-lett-Packard[J]. Interfaces, 1995, 25(5):42-63 doi: 10.1287/inte.25.5.42
[17] Oger R, Krafft A, Buffet D, et al. Geotraceability:An innovative concept to enhance conventional traceability in the agri-food chain[J]. Biotechnologie, Agronomie, Société et Environment, 2010, 14(4):633-642 http://popups.ulg.ac.be/1780-4507/index.php?id=6375
[18] 李思林.浅议我国农业行政管理体制改革创新[J].农业经济, 2016, (3):32-33 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NYJJ201603012.htm Li S L. Discussion on innovation of China's agricultural ad-ministrative management system[J]. Agricultural Economy, 2016, (3):32-33 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NYJJ201603012.htm
[19] 宋向党.系统化视角下的农业产业安全问题探讨[J].河北经贸大学学报, 2016, 37(5):121-125 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HBJM201605020.htm Song X D. Discussion on the agricultural security problem in systematic view[J]. Journal of Hebei University of Economics and Business, 2016, 37(5):121-125 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HBJM201605020.htm
[20] 张海鹏, 曲婷婷.农地经营权流转与新型农业经营主体发展[J].南京农业大学学报:社会科学版, 2014, 14(5):70-75 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NJNS201405009.htm Zhang H P, Qu T T. Agricultural land management rights transfer and development of new agricultural management entities[J]. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University:Social Sciences Edition, 2014, 14(5):70-75 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NJNS201405009.htm
[21] 程相友, 信桂新, 陈荣蓉, 等.农地流转对农业生态系统的影响[J].中国生态农业学报, 2016, 24(3):335-344 http://www.ecoagri.ac.cn/zgstny/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=2016308&flag=1 Cheng X Y, Xin G X, Chen R R, et al. Impact of farmland transfer on agro-ecosystem[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2016, 24(3):335-344 http://www.ecoagri.ac.cn/zgstny/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=2016308&flag=1
[22] 陈锡文.中国农业发展形势及面临的挑战[J].农村经济, 2015, (1):3-7 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NCJJ201501001.htm Chen X W. Agricultural development situation and the related challenges in China[J]. Rural Economy, 2015, (1):3-7 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NCJJ201501001.htm




 下载:
下载:
